The Internet of Things (IoT): Revolutionizing Connectivity and Automation
The Internet of Things (IoT): Revolutionizing Connectivity and Automation
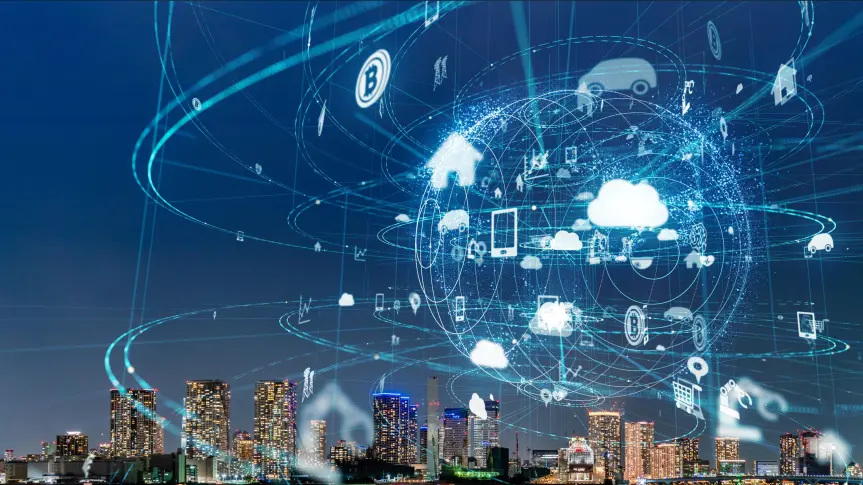
The Internet of Things (IoT) refers to the interconnected network of physical devices, vehicles, appliances, and other objects embedded with sensors, software, and connectivity capabilities that enable them to collect and exchange data. This emerging technological phenomenon has dramatically transformed various sectors, ranging from healthcare and manufacturing to transportation and home automation. The seamless integration of the physical and digital worlds through IoT is driving innovation, improving efficiency, and creating new opportunities across industries.
Key Components of IoT
-
Devices and Sensors: At the heart of IoT are the devices and sensors that collect data from the environment. These can range from simple temperature sensors to complex machinery embedded with multiple sensors that monitor various parameters.
-
Connectivity: IoT devices communicate with each other and with central systems through various connectivity technologies, including Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, cellular networks, and low-power wide-area networks (LPWAN). The choice of connectivity depends on factors such as data transmission range, power consumption, and the amount of data to be transmitted.
-
Data Processing: The vast amounts of data collected by IoT devices are processed and analyzed to extract meaningful insights. This processing can occur on the device itself (edge computing), on a central server (cloud computing), or in a hybrid model where both edge and cloud computing are utilized.
-
User Interface: The insights derived from data analysis are presented to users through various interfaces, such as mobile apps, dashboards, or automated systems. These interfaces allow users to monitor, control, and make informed decisions based on the data.
Applications of IoT
The applications of IoT are vast and varied, with significant implications for numerous industries:
-
Smart Homes: IoT has revolutionized home automation by enabling the control of lighting, heating, security systems, and appliances through connected devices. Smart home devices can be controlled remotely via smartphones, providing convenience, energy efficiency, and enhanced security.
-
Healthcare: IoT is playing a crucial role in healthcare by enabling remote monitoring of patients, managing chronic diseases, and improving the efficiency of healthcare delivery. Wearable devices can track vital signs and send data to healthcare providers, enabling timely interventions and personalized care.
-
Manufacturing: In the industrial sector, IoT is at the core of the Industry 4.0 revolution. Smart factories utilize IoT to monitor equipment performance, predict maintenance needs, and optimize production processes. This leads to reduced downtime, lower costs, and improved productivity.
-
Transportation and Logistics: IoT enhances transportation and logistics by enabling real-time tracking of vehicles and shipments. Fleet management systems use IoT to monitor vehicle health, optimize routes, and ensure timely deliveries. Smart traffic management systems reduce congestion and improve road safety.
-
Agriculture: IoT is transforming agriculture through precision farming techniques. Sensors monitor soil conditions, weather patterns, and crop health, enabling farmers to make data-driven decisions. This results in increased crop yields, reduced resource usage, and sustainable farming practices.
Challenges and Considerations
Despite its transformative potential, IoT also presents several challenges:
-
Security: The proliferation of connected devices increases the attack surface for cyber threats. Ensuring the security of IoT devices and the data they generate is a critical concern, as breaches could lead to significant disruptions or even physical harm.
-
Privacy: IoT devices collect vast amounts of personal and sensitive data. Protecting user privacy and ensuring compliance with data protection regulations are essential to maintaining trust in IoT systems.
-
Interoperability: The diversity of IoT devices and platforms can lead to interoperability issues, where devices from different manufacturers may not work seamlessly together. Standardization efforts are ongoing to address this challenge and ensure a cohesive IoT ecosystem.
-
Scalability: As the number of IoT devices grows exponentially, scaling infrastructure to manage, process, and store the vast amounts of data generated becomes increasingly challenging.
The Future of IoT
The future of IoT is poised to bring even greater connectivity, automation, and intelligence to everyday life. Emerging technologies such as 5G, artificial intelligence (AI), and blockchain are expected to further enhance IoT capabilities. 5G networks will provide faster and more reliable connections, enabling real-time data transmission and supporting a larger number of connected devices. AI will play a crucial role in analyzing IoT data, enabling predictive maintenance, autonomous systems, and personalized experiences. Blockchain technology could enhance security and transparency in IoT by providing decentralized and tamper-proof data management.
In conclusion, the Internet of Things is revolutionizing the way we live and work by connecting the physical and digital worlds in unprecedented ways. As IoT continues to evolve, it will bring about new innovations, efficiencies, and opportunities, while also posing challenges that must be addressed to realize its full potential. The successful integration of IoT into various sectors will depend on collaboration between technology providers, policymakers, and end-users to create secure, interoperable, and scalable solutions.